No relation between digit ratio (2D:4D) and visual attention patterns to sexually preferred and non-preferred stimuli
Resumen
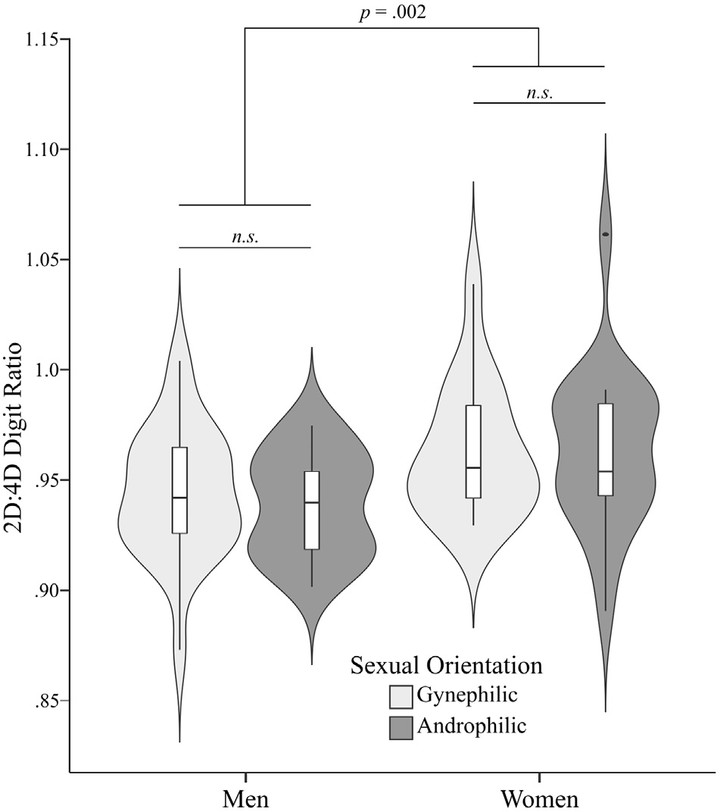
Digit ratio (2D:4D) is a marker of prenatal androgenic exposure that is correlated with different behaviour patterns. Here, we explore the relationship between 2D:4D ratio and early versus late attention to sexually preferred stimuli using an eye-tracking paradigm with 78 androphilic or gynephilic men and women. We simultaneously presented preferred and non-preferred adult stimuli and assessed visual attention across time to first fixation and total duration fixation on entire body and three specific areas (face, chest and pelvis), and investigated whether digit ratio was related to visual attentional biases towards sexually preferred stimuli. As expected, participants tended to fixate faster and for more time on the preferred gender. However, we found no significant interactions between 2D:4D and attentional biases towards the preferred gender, for any measure of attention. These results suggest that attention towards the preferred gender is not related to the 2D:4D digit ratio.