Perceived differences in social status between speaker and listener affect the speaker's vocal characteristics
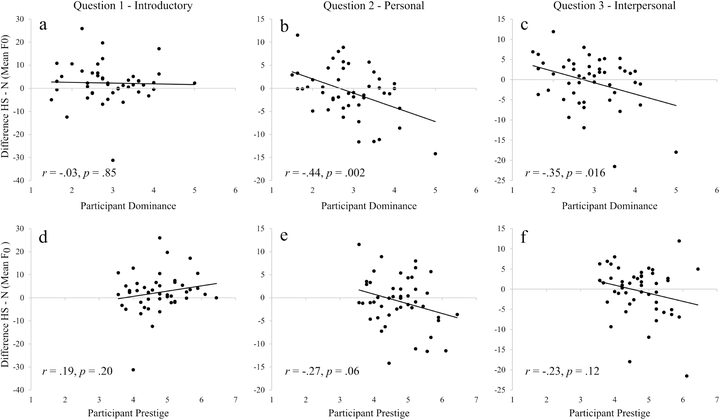 Image credit: Juan David Leongómez 2017
Image credit: Juan David Leongómez 2017Abstract
Non-verbal behaviours, including voice characteristics during speech, are an important way to communicate social status. Research suggests that individuals can obtain high social status through dominance (using force and intimidation) or through prestige (by being knowledgeable and skillful). However, little is known regarding differences in the vocal behaviour of men and women in response to dominant and prestigious individuals. Here, we tested within-subject differences in vocal parameters of interviewees during simulated job inter-views with dominant, prestigious, and neutral employers (targets), while responding to questions which were classified as introductory, personal, and interpersonal. We found that vocal modulations were apparent between responses to the neutral and high-status targets, with participants, especially those who perceived themselves as low in dominance, increasing fundamental frequency (F0) in response to the dominant and prestigious targets relative to the neutral target. Self-perceived prestige, however, was less related to contextual vocal modulations than self-perceived dominance. Finally, we found that differences in the context of the interview questions participants were asked to respond to (introductory, personal, interpersonal), also affected their vocal parameters, being more prominent in responses to personal and interpersonal questions. Overall, our results suggest that people adjust their vocal parameters according to the perceived social status of the listener as well as their own self-perceived social status.